INDIA’S FOREIGN TRADE POLICY 2023
Shri Piyush Goyal, Hon’ble Union Minister of Commerce and Industry, Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution and Textiles, announced India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2023 on 31st March saying that it is dynamic and has been kept open-ended to accommodate the emerging needs of the time. He stated that the policy had been under discussion for a long time and had been formulated after multiple stakeholder consultations. India’s overall exports, including services and merchandise exports, have already crossed US$ 750 bn and are expected to cross US$ 760 bn this year, he said. The policy sets a target of achieving exports worth $2 trillion by 2030 and outlines a broad strategy to achieve it.
The Key Approach to the policy is based on these 4 pillars: (i) Incentive to Remission, (ii) Export promotion through collaboration – Exporters, States, Districts, and Indian Missions, (iii) Ease of doing business, reduction in transaction cost and e-initiatives and (iv) Emerging Areas – E-Commerce Developing Districts as Export Hubs and streamlining SCOMET (Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) policy.
The previous foreign trade policy (FTP) was for the period 2015-20. Since 2020, no foreign trade policy was announced, though the government kept making changes. The government decided to take the views of the industry, especially exporters before finalizing a new policy. Unlike earlier years, when the FTP was valid for a period of 5 years, the new FTP has no time frame and is dynamic and flexible. Changes will be brought into the policy as and when required.
Key Facts of the Foreign Trade Policy 2023
- The FTP will no longer have a time period of 5 years but is open-ended
- The policy sets a target of achieving exports worth $2 trillion by 2030
- It emphasises export promotion through partnerships with exporters, states, districts, and Indian Missions.
- It will further encourage ease of doing business and will focus on developing areas like e-commerce and export hubs.
- The FTP 2023 would boost the growth of e-commerce export, which is estimated to reach USD 200-300 billion by 2023.
- The Foreign Trade Strategy 2023-28 includes an amnesty system for one-time settlement of export requirement defaults.
- The dairy industry will be excused from maintaining average export obligations under India’s Foreign Trade Policy.
- A special advance authorization procedure has been extended to textiles and clothing.
- Under the new regulation, the value for exports through courier services has been raised to Rs 10 lakh from Rs 5 lakh per shipment.
Process Re-Engineering and Automation
- Greater faith is being reposed on exporters through automated IT systems with risk management systems for various approvals in India’s Foreign Trade Policy. The policy emphasizes export promotion and development, moving away from an incentive regime to a regime which is facilitating, based on technology interface and principles of collaboration.
- Considering the effectiveness of some of the ongoing schemes like Advance Authorisation, EPCG etc. under FTP 2015-20, they will be continued along with substantial process re-engineering and technology enablement for facilitating the exporters.
- India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2023 codifies implementation mechanisms in a paperless, online environment, building on earlier ease-of-doing-business initiatives. Reduction in fee structures and IT-based schemes will make it easier for MSMEs and others to access export benefits.
- Duty exemption schemes for export production will now be implemented through Regional Offices in a rule-based IT system environment, eliminating the need for a manual interface. During the FY23-24, all processes under the Advance and EPCG Schemes, including issue, re-validation, and EO extension, will be covered in a phased manner. Cases identified under the risk management framework will be scrutinized manually, while a majority of the applicants are expected to be covered under the ‘automatic’ route initially.
 Towns of Export Excellence
Towns of Export Excellence
Places like Faridabad, Moradabad, Mirzapur, and Varanasi have been designated as new Towns of Export Excellence (TEE) under India’s Foreign Trade Policy in addition to the existing 39 towns. The TEEs will have priority access to export promotion funds under the MAI scheme and will be able to avail of Common Service Provider (CSP) benefits for export fulfilment under the EPCG Scheme. This addition is expected to boost the exports of handlooms, handicrafts, and carpets.
Recognition of Exporters
- Exporter firms recognized with ‘status’ based on export performance will now be partners in capacity-building initiatives on a best-endeavour basis.
- Similar to the ‘each one teach one’ initiative, 2-star and above status holders would be encouraged to provide trade-related training based on a model curriculum to interested individuals.
- This will help India build a skilled manpower pool capable of servicing a $5 Trillion economy before 2030.
- Status recognition norms have been re-calibrated to enable more exporting firms to achieve 4 and 5-star ratings, leading to better branding opportunities in export markets.
Promoting export from the districts
- India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2023 aims at building partnerships with State governments and taking forward the Districts as Export Hubs (DEH) initiative to promote exports at the district level and accelerate the development of the grassroots trade ecosystem.
- Efforts to identify export-worthy products & services and resolve concerns at the district level will be made through an institutional mechanism – State Export Promotion Committee and District Export Promotion Committee at the State and District level, respectively. District-specific export action plans to be prepared for each district outlining the district-specific strategy to promote the export of identified products and services.
Streamlining SCOMET Policy
- India is placing more emphasis on the “export control” regime as its integration with export control regime countries strengthens.
- There is a wider outreach and understanding of SCOMET (Special Chemicals, Organisms, Materials, Equipment and Technologies) among stakeholders, and the policy regime is being made more robust to implement international treaties and agreements entered into by India.
- A robust export control system in India would provide access to dual-use High-end goods and technologies to Indian exporters while facilitating exports of controlled items/technologies under SCOMET from India.
Facilitating E-Commerce Exports
- E-commerce exports are a promising category that requires distinct policy interventions from traditional offline trade. Various estimates suggest e-commerce export potential in the range of $200 to $300 billion by 2030.
- India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2023 outlines the intent and roadmap for establishing e-commerce hubs and related elements such as payment reconciliation, bookkeeping, returns policy, and export entitlements.
- As a starting point, the consignment-wise cap on E-Commerce exports through courier has been raised from ₹5Lakh to ₹10 Lakh in India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2023.
- Integration of Courier and Postal exports with ICEGATE will enable exporters to claim benefits under this policy.
- The comprehensive e-commerce policy addressing the export/import ecosystem would be elaborated soon, based on the recommendations of the working committee on e-commerce exports and inter-ministerial deliberations
- Extensive outreach and training activities will be taken up to build the capacity of artisans, weavers, garment manufacturers, gems and jewellery designers to onboard them on E-Commerce platforms and facilitate higher exports.
 Facilitation under the Export Promotion of Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme
Facilitation under the Export Promotion of Capital Goods (EPCG) Scheme
The EPCG Scheme, which allows the import of capital goods at zero Customs duty for export production, is being further rationalized. Some key changes being added are:
- Prime Minister Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel Parks (PM MITRA) scheme has been added as an additional scheme eligible to claim benefits under the CSP (Common Service Provider) Scheme of EPCG.
- Dairy sector to be exempted from maintaining Average Export Obligation – to support the dairy sector to upgrade the technology.
- Battery Electric Vehicles (BEV) of all types, Vertical Farming equipment, Wastewater Treatment and Recycling, Rainwater harvesting system and Rainwater Filters, and Green Hydrogen are added to Green Technology products – will now be eligible for reduced Export Obligation requirements under the EPCG Scheme.
Facilitation under the Advance Authorization Scheme
The advance authorisation Scheme accessed by DTA units provides duty-free import of raw materials for manufacturing export items and is placed at a similar footing to EOU and SEZ schemes. However, the DTA unit has the flexibility to work both for domestic as well as export production. Based on interactions with industry and Export Promotion councils, certain facilitation provisions have been added in the present FTP such as:
- Special Advance Authorisation Scheme extended to export of Apparel and Clothing sector under para 4.07 of HBP on a self-declaration basis to facilitate prompt execution of export orders – Norms would be fixed within a fixed timeframe.
- Benefits of Self-Ratification Scheme for fixation of Input-Output Norms extended to 2 stars and above status holders in addition to Authorised Economic Operators at present.
Merchanting trade
- To develop India into a merchanting trade hub, India’s Foreign Trade Policy 2023 has introduced provisions for merchanting trade. Merchanting trade of restricted and prohibited items under the export policy would now be possible.
- Merchanting trade involves the shipment of goods from one foreign country to another foreign country without touching Indian ports, involving an Indian intermediary.
- This will be subject to compliance with RBI guidelines, and won’t be applicable for goods/items classified in the CITES and SCOMET list.
- In course of time, this will allow Indian entrepreneurs to convert certain places like GIFT City etc. into major merchanting hubs as seen in places like Dubai, Singapore and Hong Kong.
Conclusion
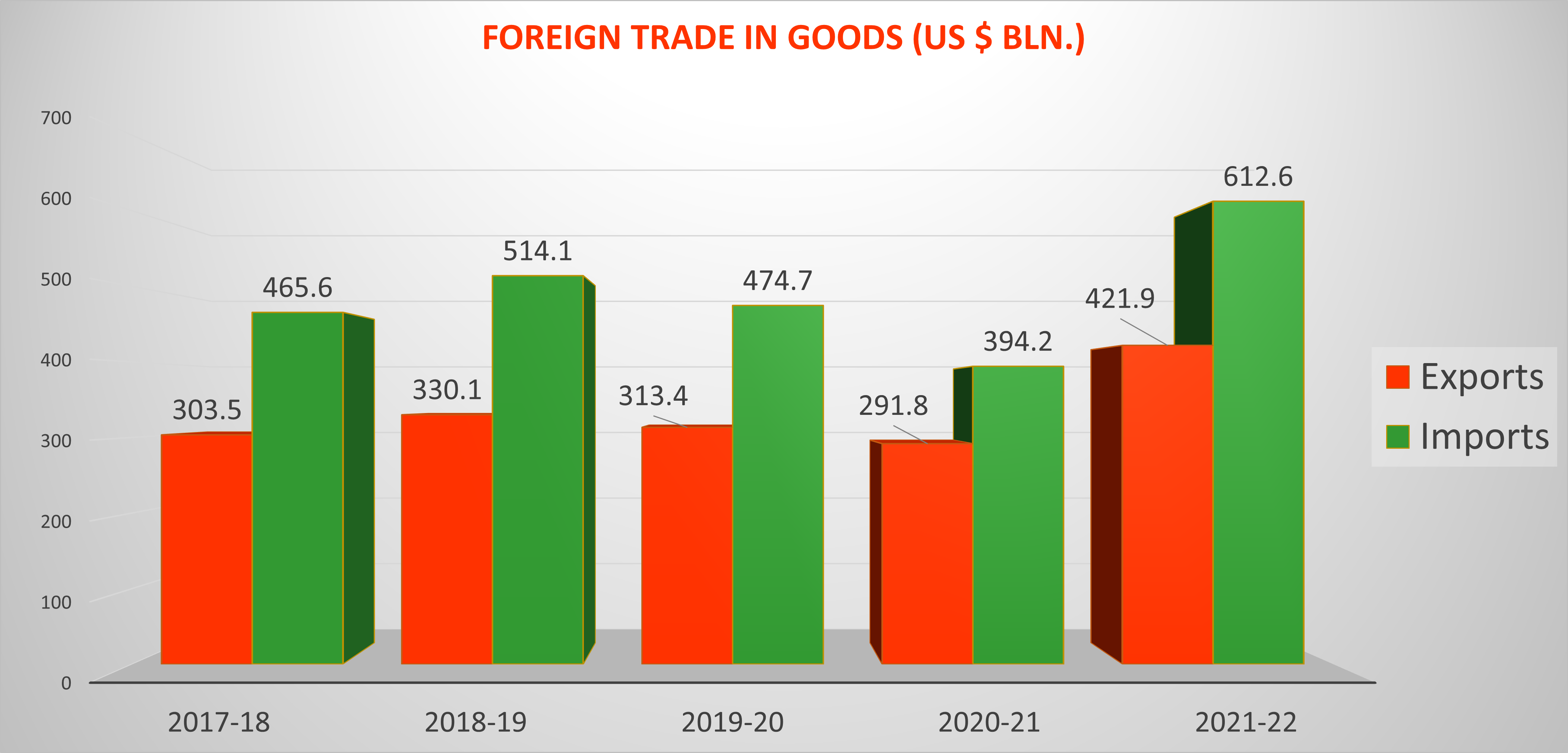
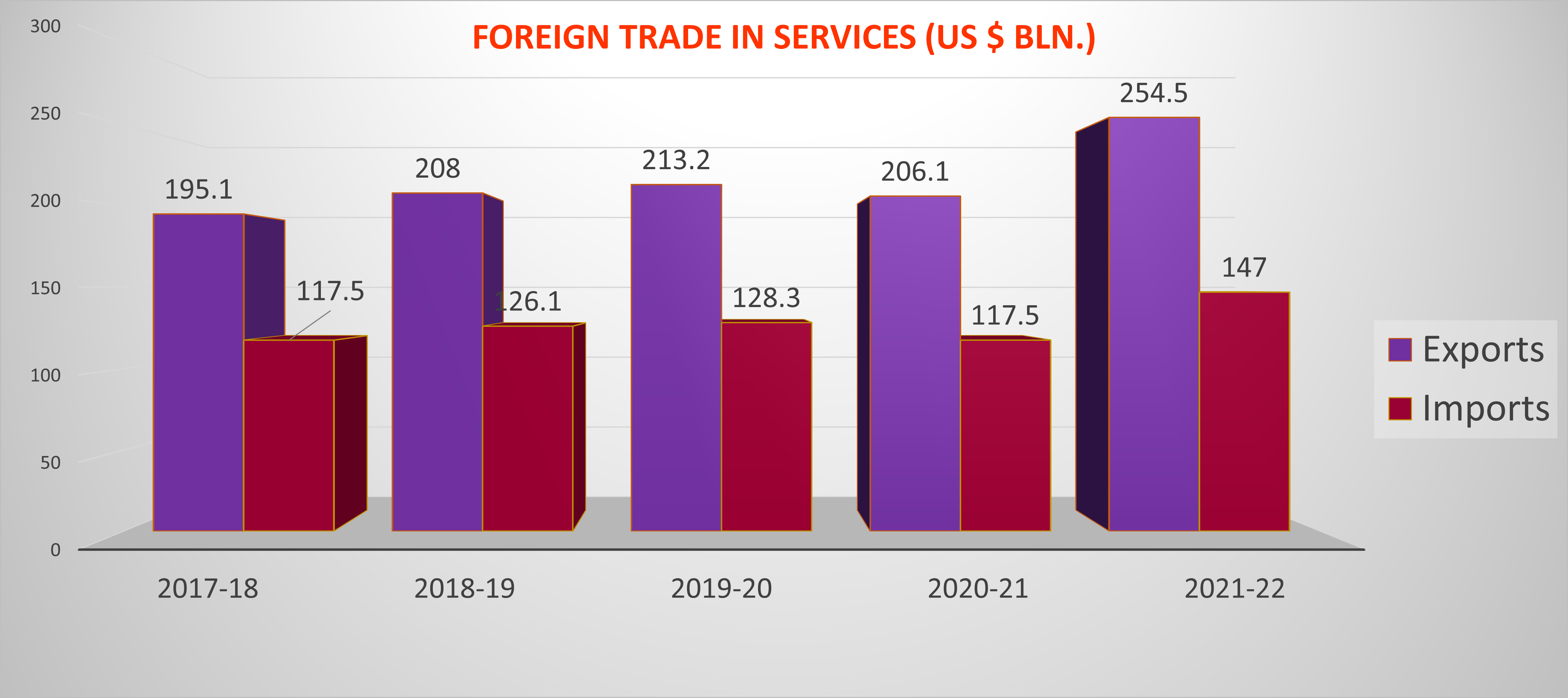
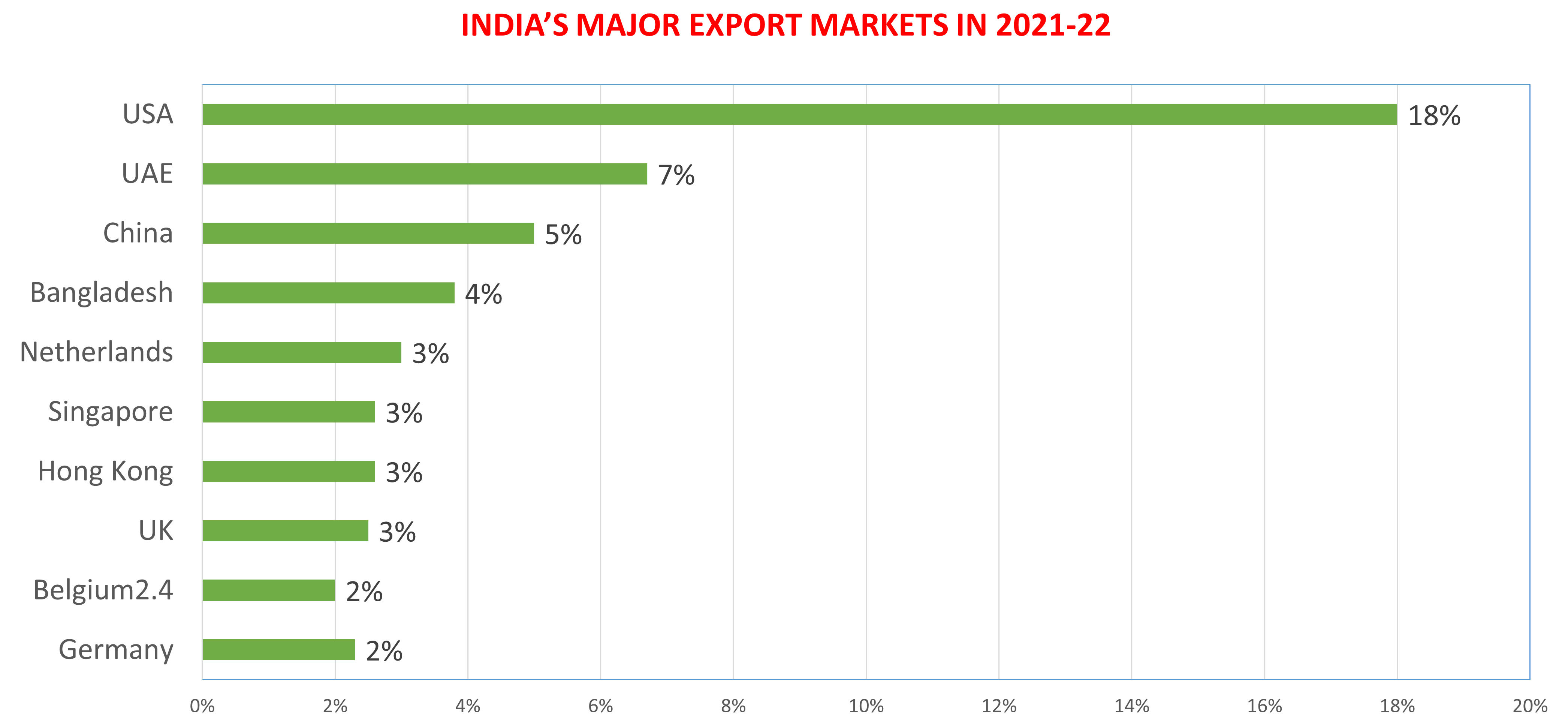
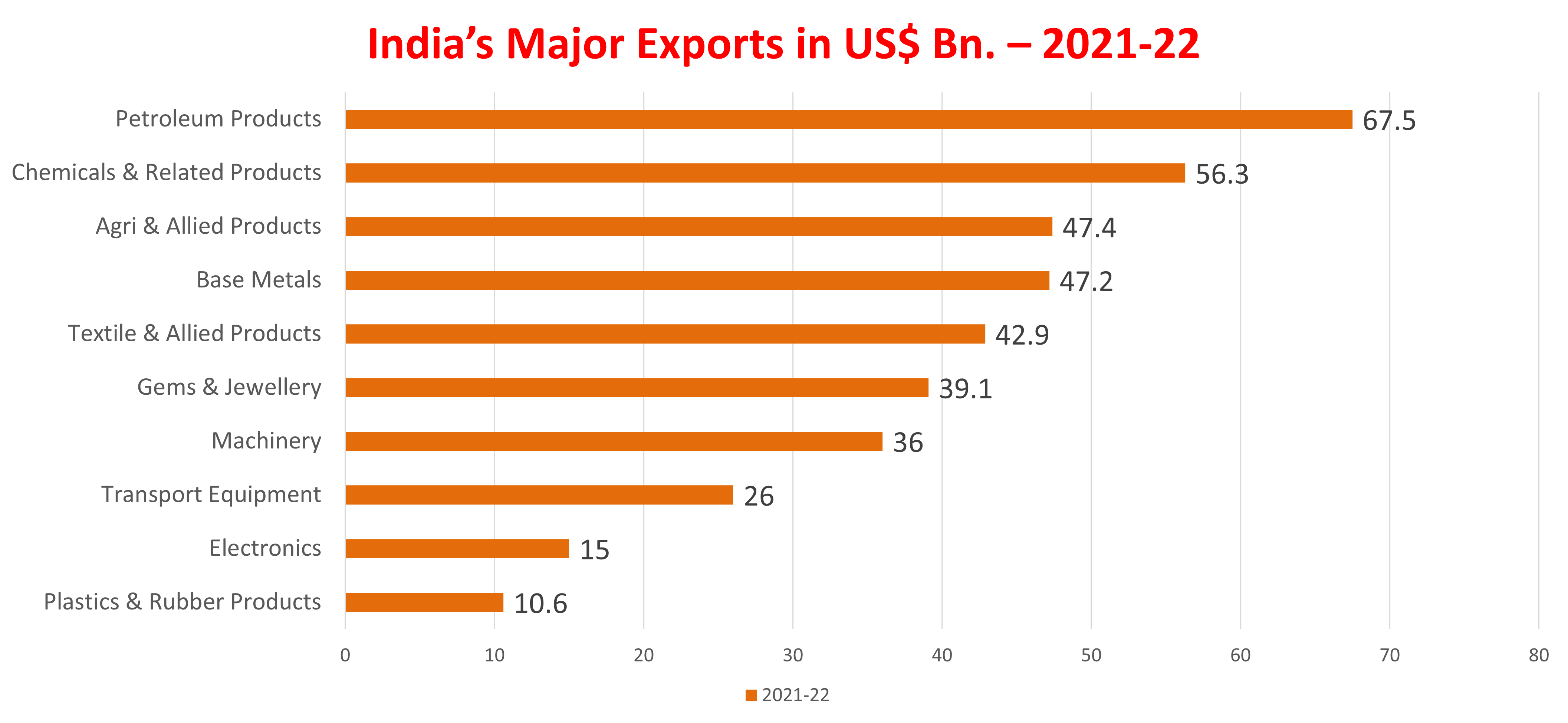
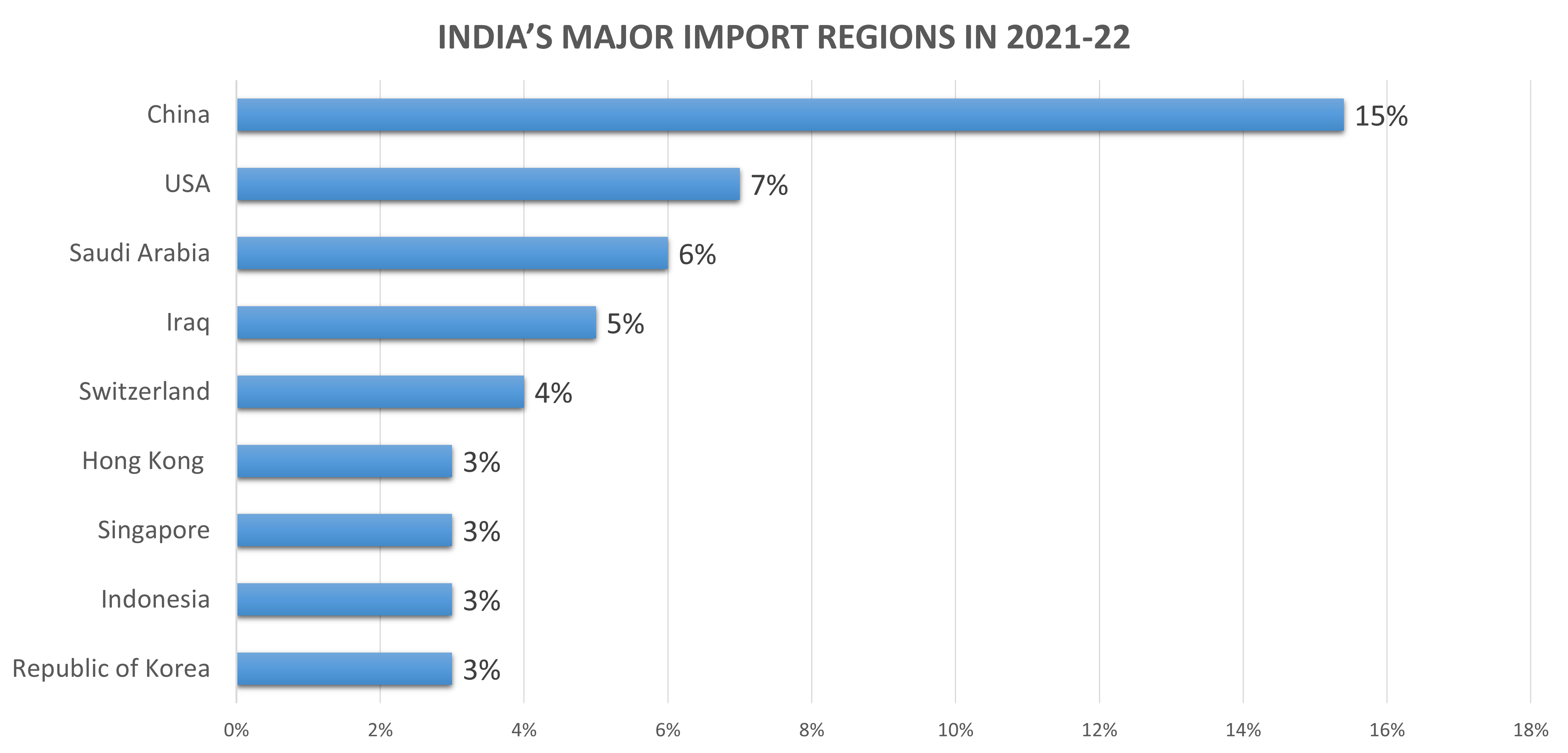
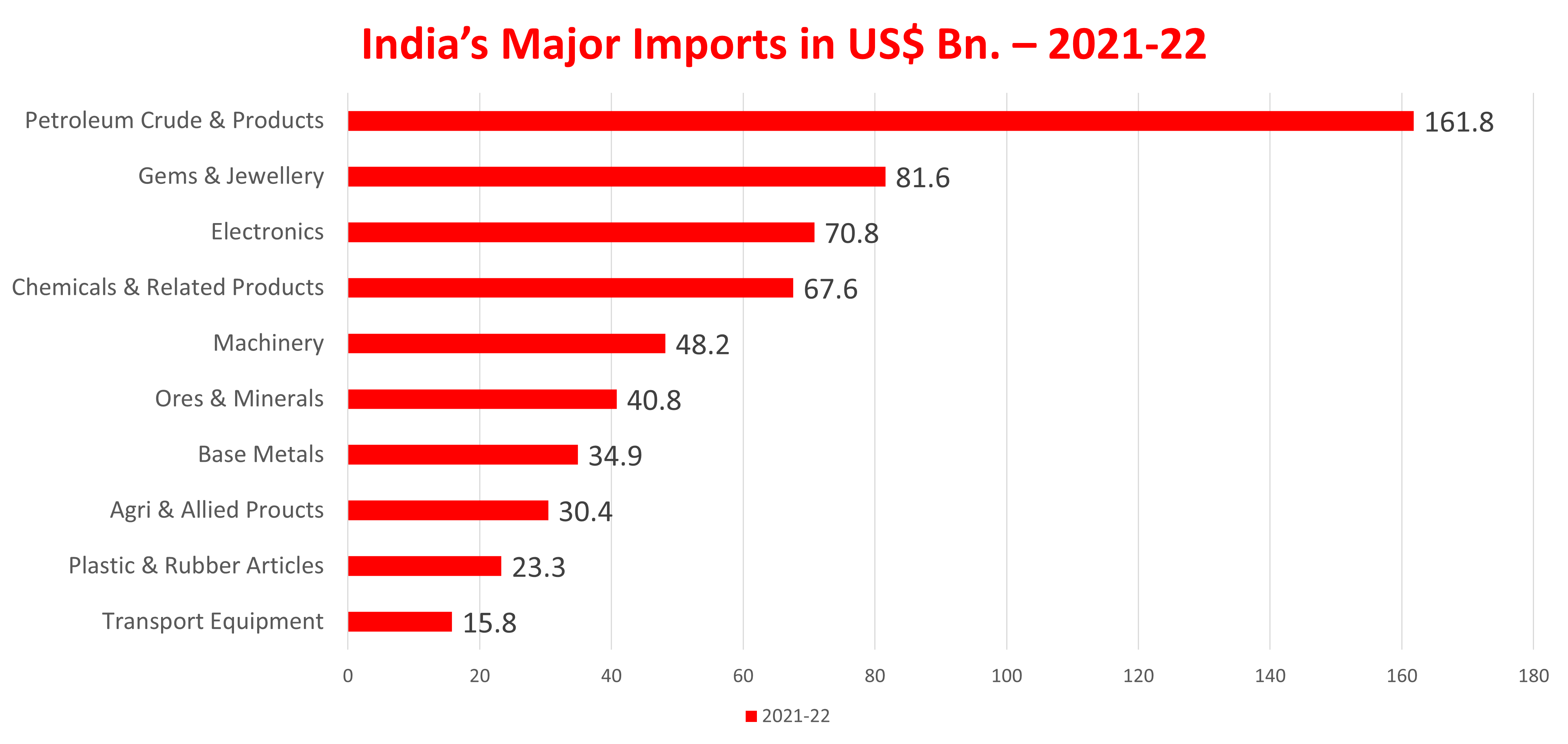
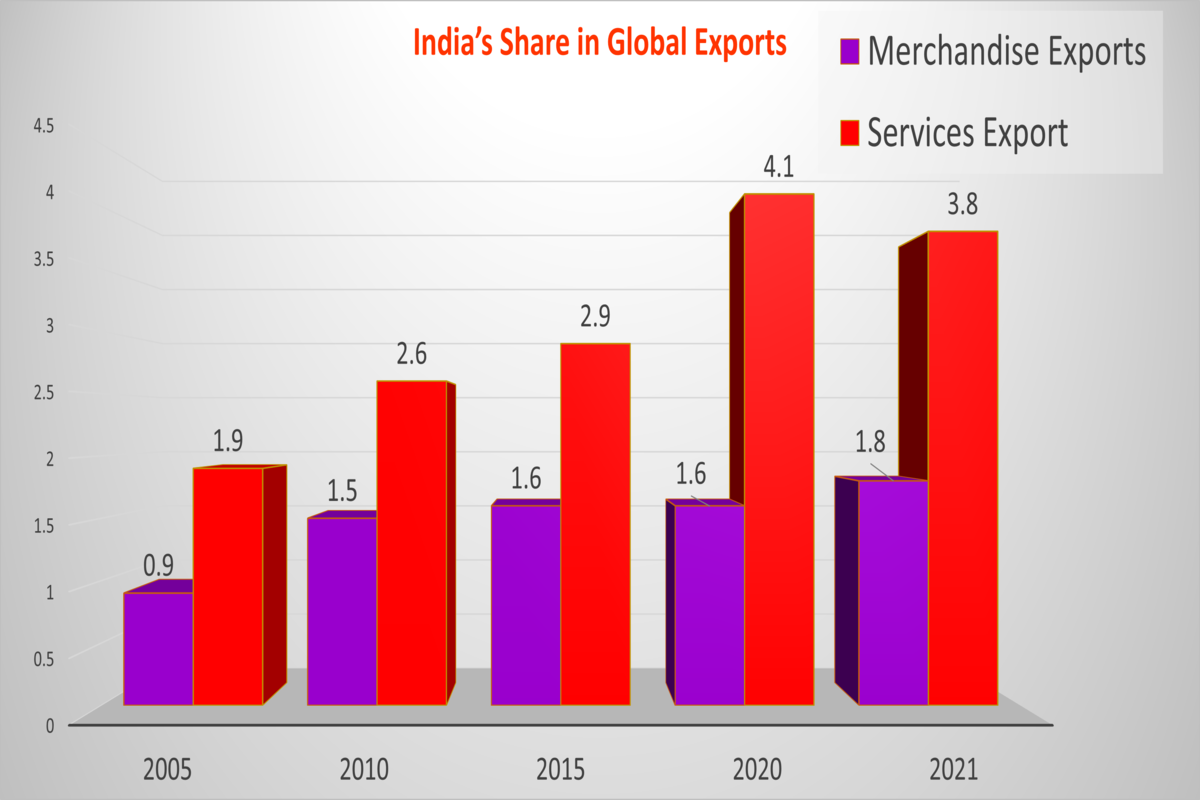
Though India’s Foreign Trade Policy is welcome and it contains some good developments, it still does not outline a grand strategy for increasing India’s exports in a big way. India continues to be heavily dependent on its domestic market and India’s foreign trade is very small compared to the size of its economy. The above chart shows that India has not progressed much in terms of increasing its share in global trade. India’s share of merchandise exports in 2021 was only 1.8% of global trade and its commercial services exports were 3.8%. India has done reasonably well in terms of service exports but has not been able to enhance and elevate its manufacturing exports.
Considering that India is the largest country by population and the sixth largest economy in the world, India’s share in global trade should be much higher. This is even more important as India aims to be a global economic power. India’s Foreign Trade Policy does not address this issue in any significant way nor does it outline any vision or strategy to achieve its goals.
Many foreign trade experts and economists have been critical of India’s Foreign Trade Policy. They feel that the policy has no clear focus and does not outline a vision for promoting India’s merchandise exports. The policy also has not taken into account the emerging trade blocks led by countries like China and other geopolitical developments that can affect India’s exports.
The policy has no clear strategy on how it would achieve the target of $ 2 trillion worth of exports by 2030, considering the fact that India’s exports in FY 2022 stood only at $760 billion. The focus of the policy appears to be more on regulations, laws and government schemes rather that any attempt to give a boost to MSMEs and other large exporters by eliminating the debilitating and growth-suppressing regulations.
Also, there is no clear strategy to become less protectionist and reduce customs duties. This is very important as India continues to be one of the most protectionist countries in the world. Also, very strangely, India’s Foreign Trade Policy contains no mention of India’s thrust on signing Free trade Agreements (FTAs). Without the FTAs with major regions such as the European Union, North America, and the ASEAN region, not much will be achieved in terms of boosting India’s exports or achieving the target of $ 2 trillion by 2030.
Source – Press Information Bureau, Government of India
About the Author
 |
VIJAY KUMAR VADDADI, India Entry & International Affairs
Mr. Vijay Kumar is an Industrial Economist with 35+ years of experience in Economic Analysis, Trade & Investment Promotion, International Business Strategy & Cross-Cultural Impact. A Post-Graduate in Economics with specialization in Industrial Economics and Economics of Transportation, Public Utilities & Social Infrastructure from the University of Bombay (1982). In 1984, he joined the Consulate General of the Netherlands in Mumbai as an Economic & Commercial Officer and continued his association with the Netherlands Government (NBSO) for over 30 years. At SAS Partners, he heads the Trade and Investment Promotion activities, supports organising programmes for international business delegations, curates knowledge reports, and market studies and also helps our international clients in understanding the Indian business landscape better. |